네트워크 구조를 구성하는 몇 가지 네트워크 표준 준수 디바이스가 있다. 네트워크 크기에 따라 이러한 디바이스 중 몇 가지를 사용하여 네트워크의 백본을 구축할 수도 있다. 이러한 연결 디바이스들은 주로 LAN 또는 WAN 을 연결하기 위한 장치라 할 수 있다.
이러한 디바이스들은 대부분 MAC(Media Access Control) 주소나 IP 주소를 사용하여 네트워크 상의 데이터를 전달한다.
MAC 주소? IP 주소? :[Network] - [Network] MAC 주소 와 IP 주소
[Network] MAC 주소 와 IP 주소
What is a media access control address? 미디어 액세스 제어(MAC) 주소는 제조 시점에서 모든 네트워크 지원 디바이스에 할당하는 고유 식별자이다. 내장된 주소, 이더넷 하드웨어 주소 또는 실제 주소라고
buildgoodhabit.tistory.com
리피터
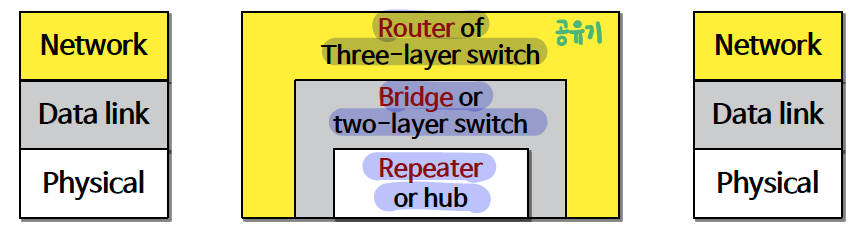
리피터는 네트워크 신호를 반복하는 2포트 디바이스. OSI 7 Layer7 중 Physical Layer 에서 동작
전송거리에 따른 신호의 감쇄를 보완하기 위해 만든 장비이다 : 작아진 신호를 수신하여 원래의 정보로 복원한 이후에 다시 신호로 변환하여 전송한다. 즉, 신호의 전송거리를 증가시킨다.
리피터는 네트워크 장치가 서로 멀리 떨어져 있을 때 사용.
리피터는 데이터 패킷을 재전송하기 전에는 패킷을 수정하거나 해석하지 않으며, 신호를 증폭하지도 않음. 대신 원래 강도(비트)로 데이터 패킷을 다시 생성.
A repeater is a two-port device that repeats network signals. Repeaters are used when network devices are some distance from each other. The repeater doesn't modify or interpret data packets before it resends them, and it doesn't amplify the signal. Instead, it regenerates the data packet at the original strength, bit by bit.
허브
허브는 네트워크에서 다중 포트 리피터 역할을 한다. 허브는 둘 이상의 디바이스를 연결하고 네트워크 레이아웃을 구성하는 데 사용한다. 예를 들어 허브를 계단식 배열하여 네트워크 분기를 만들거나, 엔드포인트로 사용해 여러 사용자 유형 디바이스가 있는 별모양 레이아웃을 만들 수 있다. 허브에는 허브와 네트워크 디바이스 간의 입력/출력 이더넷 연결 역할을 하는 여러 포트가 포함되어 있다. 허브는 정해진 속도, 즉 네트워크에서 가장 느린 네트워크 디바이스의 속도로만 작동한다. 허브는 데이터 패킷을 해석하거나 필터링하지 않으며, 연결된 모든 디바이스에 각 데이터 패킷의 복사본을 보낸다. Physical layer에서 동작
A hub acts as a multiport repeater on a network. Hubs are used to connect more than one device and structure the layout of a network. For example, you can cascade hubs to create network branches or as an endpoint to create a star layout with multiple user type devices. Hubs contain multiple ports that act as an input/output Ethernet connection between the hub and a network device. A hub can operate at only one speed, which is the speed of the slowest network device on the network. It doesn't interpret or filter data packets and sends copies of each data packet to all attached devices.
허브 유형
고속 이더넷: 이 허브는 100Mbps 네트워크에 사용하며 클래스 I 및 클래스 II 유형의 허브로 제공된다. 두 클래스의 주요 차이점은 데이터 전송 지연 시간이다. 클래스 I 허브에서는 최대 140비트 타임의 신호 지연이 발생한다. 클래스 II 허브의 지연 시간은 최대 96비트 타임이다. 지연이 있어야 서로 다른 기본 유형 간의 데이터 코드 변환이 가능하다. 허브 기반 네트워크에서는 클래스 II 허브 두 개만 사용할 수 있다. 클래스 II 허브는 속도가 빠르기 때문에 패킷 충돌 가능성을 높인다.
이중 속도: 기존 허브 네트워크에서는 연결된 네트워크 디바이스 중 가장 느린 디바이스가 네트워크 속도를 제어했었다. 예를 들어 네트워크에 10Mbps 및 100Mbps 장치가 연결되어 있다면, 전체 네트워크의 속도는 10Mbps밖에 되지 않는다. 이중 속도 허브는 속도가 다른 두 디바이스 사이에서 브리지 역할을 하여 이 문제를 해결한다.
허브는 몇몇 디바이스의 소규모 애드혹 네트워크에 사용하며 엔터프라이즈 수준에서는 거의 사용되지 않는다. 실질적으로는 OSI 7 Layer7 1-3 계층까지 허브가 사용된다.
Fast Ethernet: This hub is used for 100-Mbps networks and comes as Class I and Class II type hubs. The primary difference between the two is the amount of delay in data transmission. A Class I hub introduces a signal delay of up to 140-bit times. A Class II hub has a delay of up to 96-bit times. The delay allows for the transcoding of data between different base types. Only two Class II hubs can be used in a hub-based network. Class II hubs increase the likelihood of packet collisions because of their higher speeds.
Dual speed: With a traditional hub network, the speed of the network was governed by the slowest network device attached. For example, if you had 10-Mbps and 100-Mbps devices connected to a network, the speed of the whole network was only 10 Mbps. Dual-speed hubs solve the problem by acting as a bridge between the two different-speed devices.
Hubs are used for small ad-hoc networks of a few devices, but they're rarely used at an enterprise level.
브리지
브리지는 네트워크를 네트워크 세그먼트로 나누고, 해당 세그먼트 간에 데이터 패킷을 필터링 및 전달 가능. 브리지는 네트워크 디바이스의 MAC 주소를 사용하여 데이터 패키지의 대상을 결정. 일반적으로 브리지는 네트워크 세그먼트 상의 불필요한 네트워크 트래픽을 줄여 네트워크 성능을 개선하는 용도로 사용한다. data-link layer에서 사용. 프레임 내의 주소값을 읽어서 이에 따른 동작을 수행함으로 보다 지능적인 서비스를 제공한다.
A bridge divides a network into network segments and can filter and forward data packets between these segments. Bridges use the network device's MAC address to decide the data package's destination. Typically, a bridge is used to improve network performance by reducing unnecessary network traffic on network segments.
스위치
스위치는 브리지와 허브의 기능을 결합한 것이다. 네트워크를 세그먼트화하고 패킷 데이터를 해석 및 필터링하여 연결된 네트워크 디바이스로 직접 보낼 수 있다. 스위치는 네트워크 디바이스의 MAC 주소를 사용하여 데이터 패키지의 대상을 결정한다. 스위치는 전이중 모드로 작동한다. 따라서 네트워크 디바이스와의 데이터 전송 및 수신을 동시에 처리할 수 있다. data-link layer에서 사용
A switch combines the functionality of a bridge and a hub. It segments networks and can interpret and filter packet data to send it directly to an attached network device. Switches use the network device's MAC address to decide the data package's destination. A switch operates in full-duplex mode, which means it can send and receive data to and from network devices at the same time.
스위치 : 1대 N 통신이 가능
허브 : 1 대 1 통신 가능
기능
최신 이더넷 기반 스위치는 이더넷 허브보다 더 많은 기능을 제공
이더넷 스위치는 대상 네트워크의 연결 속도에 맞게 인바운드 패킷의 연결 속도를 조정
현재 많은 스위치가 PoE(Power over Ethernet)를 지원. PoE를 사용하면 VoIP(Voice over IP) 휴대폰 같은 네트워크 디바이스가 별도의 전원 공급 장치 없이도 스위치에서 전원을 공급받음
다른 모듈을 스위치에 연결하여 포트 미러링, 패킷 스니퍼 및 침입 탐지 시스템 같은 기능을 사용할 수 있다.
Learning : 호스트들의 정보를 테이블에 저장하는 기능, Unicast, Multicast, Broadcast 프레임의 Source Mac 주소를 Switch의 Mac Addr Table 에 등록하는 것, PC 간에 ARP 프레임과 응답 프레임을 주고 받으면서 스위치는 Mac Addr Table 에 정보를 저장한다.
Flooding : 모든 정보를 호스트에 뿌리는 것. 즉, 입력된 포트를 제외한 모든 포트로 정보가 전달되는 것을 말한다. Aging에 의해 목적지 Mac 주소가 테이블에 없는 Unicast 정보도 flooding 된다. 어떤 주소가 테이블에 없는 경우 그냥 다 뿌려 버린다
Forwarding : 알고있는 목적지에 정보를 전달하는 것
Filtering : flooding 시에 어떤 호스트에 대해 Mac Addr Table 정보가 있고 그 주소가 받는 주소가 아니라면 그곳을 제외하고 전송하는 것을 말한다.
Aging : 일정시간이 지나면 Mac Addr Table 정보를 비우는 작업을 한다.
Modern Ethernet-based switches offer more functionality and capabilities than an Ethernet hub.
An Ethernet switch can adjust the connection speed of an inbound packet to match the connection speed of the destination network.
Many switches now support Power over Ethernet (PoE). PoE enables network devices like Voice over IP (VoIP) phones to get power from the switch, without needing a separate power supply.
Other modules can be attached to the switch to enable functions like port mirroring, packet sniffers, and intrusion detection systems.
라우터
라우터는 원거리 주소가 다른 여러 네트워크를 연결한다. 데이터 패킷을 해석 및 필터링한 후, 올바른 네트워크에 전달. 라우터는 네트워크 디바이스의 IP 주소 정보를 사용하여 데이터 패키지를 관련 대상으로 라우팅한다. 현재 대부분의 라우터는 연결된 네트워크로 전달되는 데이터 트래픽 관련 문제를 탐지하고, 문제가 되는 부분을 우회해 라우팅하거나 다시 라우팅할 수 있다. 라우터는 게이트웨이라고도 함. 네트워크 디바이스를 구성할 때는 대부분 기본 게이트웨이 IP 주소를 사용하여 구성하게 된다. OSI Layer 7 d의 네트워크 계층에서 사용하는 주소 값을 검사하고 사용한다. 서로 독립적인 LAN 과 LAN 을 연결하거나 LAN 과 WAN을 연결할 때 사용함.
Routers link networks with different ranged addresses together. They can interpret and filter data packets, and then forward them to the correct network. Routers use the network device's IP address information to route the data package to its destination. Most routers can now detect issues with data traffic that flows to any attached network and route or reroute it around the issue. A router is also called a gateway. When you configure network devices, you'll usually configure it with a default gateway IP address.
내부 네트워크 - 방화벽, 라우터 안쪽을 의미한다. Serial Interface
외부 네트워크 - 방화벽, 라우터 바깥쪽을 의미한다. ethernet interface
** [라우팅/ routing] : 어떤 네트워크에서 통신을 보낼 때 최적의 경로를 찾는 것을 말한다.
상호 연결
상호 연결된 네트워크의 라우터는 각 네트워크 간의 기본 경로를 나열하는 경로 지정 테이블을 유지 관리. 라우터는 네트워크에 있는 모든 네트워크 디바이스에 대한 권한 시작 역할을 한다. 라우팅 정보는 BGP(Border Gateway Protocol) 같은 라우팅 프로토콜을 사용하여 라우터 사이에서 공유된다.
Routers in an interconnected network maintain a routing table that lists the preferred route between each of the networks. The router acts as the start of authority for all the network devices on its network. Routing information is shared between routers by using a routing protocol like the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
유형
대부분의 라우터는 BGP를 사용하여 라우팅 정보를 공유. 공유되는 정보 유형은 라우터의 사용 방법 및 사용하는 기능에 따라 다르다.
다양한 네트워크 요구 사항을 처리하는 데 사용하는 몇 가지 고유한 분류 또는 라우터 유형이 존재.
액세스 라우터: 일반적으로 홈 오피스 또는 소형 위성 사무소에서 사용하는 이 라우터는 대부분 단순한 라우팅 요구를 충족하는 저렴한 디바이스
배포 라우터: 여러 라우터의 트래픽 라우팅 데이터를 컴파일. 배포 라우터는 중요한 요소인 메모리와 처리 능력을 제공. 이 유형의 라우터는 방대한 양의 라우팅 정보를 저장하도록 설계됨. WAN에서 서비스 품질을 관리하고 제어하는 용도로 자주 사용됨.
에지 라우터: 에지 라우터는 사용자 네트워크와 다른 네트워크(예: 사용자의 로컬 네트워크와 인터넷) 간의 경계에서 작동. 트래픽을 필터링하고, 패킷 헤더를 기준으로 내부적으로 라우팅하거나 전달하는 게이트웨이 역할을 한다. 대부분의 에지 라우터는 보안 강화를 위해 액세스 제어 또는 방화벽과 함께 제공. 그리고 DHCP 및 DNS 서비스도 처리.
라우터: 엔터프라이즈 라우터라고도 하는 이 라우터는 높은 대역폭용으로 설계됨. 여러 건물 또는 지리적 위치를 연결하는 데 사용된다. 핵심 라우터는 패킷 손실을 최소화하고 정체를 방지하는 데 중점을 두기 때문에, 에지 라우터에 비해 대체로 기능 수가 적으며 에지 라우터로 패킷을 전달 가능하다.
The majority of routers use the BGP to share routing information. The type of information shared depends on the usage of the router and the functions they use.
There are several distinct classifications or types of routers available to service different network needs.
Access routers: Typically used in a home or small satellite offices, these routers tend to be low-cost devices with a simple routing need
Distribution routers: These routers compile traffic routing data from multiple routers. Distribution routers come with more significant memory and processing power. This type of router is designed to hold vast quantities of routing information. It's often used to manage and control the quality of service across a WAN.
Edge routers: An edge router operates at the boundary between your network and other networks, for example, your local network and the internet. They act as gateways to filter traffic and route it internally or forward it based on the packet header. An edge router often comes with access control or firewalls to improve the security. It might also handle DHCP and DNS services.
Core routers: Sometimes called enterprise routers, these routers are designed for higher bandwidths. They're used to connect different buildings or geographic locations together. Core routers tend to have fewer features than edge routers because their primary focus is on minimizing packet loss and preventing congestion. They tend to do packet forwarding to edge routers.
무선 라우터
이 네트워크 디바이스는 일반 액세스 라우터의 모든 라우팅 기능에 더해 무선 액세스 지점 기능까지 제공. 무선 라우터 또는 무선 액세스 지점은 유선이 아닌 네트워크 연결을 제공하도록 설계됨. 인터넷 또는 다른 네트워크에 액세스하는 모든 프로비저닝은 네트워크에 연결된 에지 라우터가 처리한다. 무선 라우터를 사용하면 무선 로컬 영역 네트워크이라고 하는 다른 유형의 네트워크를 구축할 수 있다.
무선 라우터를 무선 모뎀과 혼동해선 안 된다. 무선 모뎀은 가정 또는 사무실의 ISP가 제공하며, ISP에서 보내는 신호를 컴퓨터 네트워크에서 사용할 수 있는 신호로 변환하는 디바이스이다. 일반적으로 무선 모뎀은 라우터와 함께 사용해 개인 가정 또는 사무실 네트워크를 만든다.
This network device provides all the routing capabilities of a regular access router, but it also offers wireless access point functions. A wireless router or wireless access point is designed to provide a non-wired connection to your network. Any provision to access the internet or other networks is handled by an edge router associated with your network. A wireless router lets you build a different type of network called a wireless local area network.
A wireless router shouldn't be confused with a wireless modem. A wireless modem is what you receive from your ISP for your home or office and is the device that converts the signal from the ISP into one that's usable on a computer network. Wireless modems are typically combined with routers to allow you to create a private home or office network.
Reference
출처 1 : docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/network-fundamentals/3-network-infrastructure
Types of network devices to use when you build a network - Learn
Explore network standards and the purpose and use of repeaters, hubs, switches, and routers that are used to build networks.
docs.microsoft.com
'Network' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Network] 메세지 전송방식 : 유니캐스트, 멀티캐스트, 브로드 캐스트 (0) | 2021.01.25 |
|---|---|
| [Network] OSI 7 Layer 개념 overview (0) | 2021.01.14 |
| [Network] MAC 주소 와 IP 주소 (0) | 2021.01.11 |
| [Network] ethernet 이더넷 (0) | 2021.01.11 |
| [Network] Network Type and Topologies (0) | 2021.01.08 |